After several months of development the Document Data-Tracking Client was released last week. It is an open-source desktop client application for the TraSer server and it is build upon the GUI4j framework. Also, it is available for download on Source Forge.
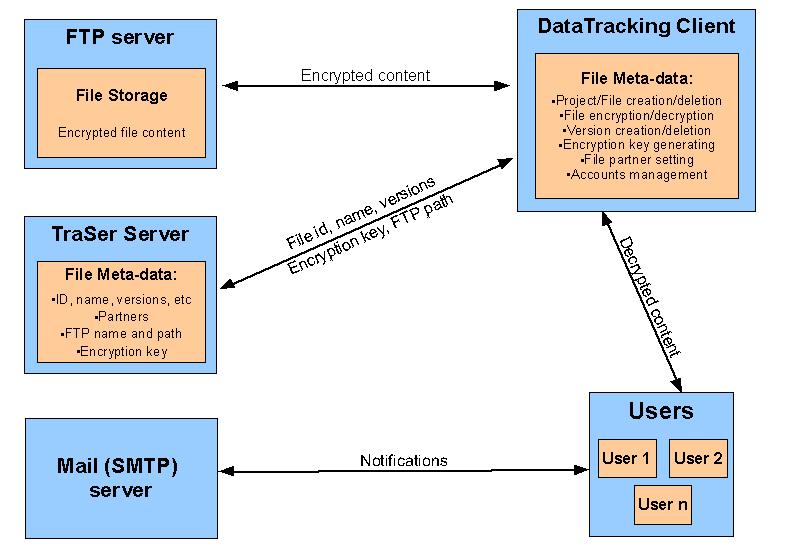
The Data-Tracking client uses the TraSer server to store meta-data for projects, files, and file versions while the actual files contents are stored on a FTP server. The access details to this FTP server that can be configured at startup. The contents of the files are encrypted by the client and stored in this way the FTP server while the encryption key is stored in the TraSer server along with other meta-data. This encryption is performed to avoid unauthorized modifications of the files in case somebody accesses the FTP server directly. The Data-Tracking Client also uses a mail server to send notifications to the users. The SMTP settings can also be specified at application startup in the configuration file.
Each file can have several partners (users that have different kind of access to it, beside the author). When a file is modified (a new version is created) all the partners are notified via e-mail. The next image illustrates the concept behind this and is also an overall picture of the architecture.
Following, I will describe the process of adding a new file to he repository and the process of creating a new file version to better illustrate the architecture.
When a user presses the Submit button for a new file the following occurs:
- the a new entry is generated on the TraSer server which is populated with the new file meta-data: file-name, description, parent-project, partners, and other general info, encryption key and the name and path that this file will have on the FTP server where the actual content is stored.
- the file content is encrypted and stored on the FTP server under the name and path specified in the file meta-data
- all the users are notified about the new file creation via e-mail
A new version of the file appears when the a file is checked out modified and checked back in. There are two types of check-out operations: serial and parallel. The difference between them is that in serial mode the file is locked on the server so nobody can check it out until it is checked back in by the first user.
When a user checks out a file the following occurs:
- the FTP name and path of the file along with the encryption key is retrieved from the server
- the file’s content is loaded from the FTP, decrypted and saved in a local folder that is selected by the user and saved internally by the application
- the user can open the file from that location and do any required modifications
After modifying the file on the local disk the user can check in the file. The following occurs:
- a new file version is created using the file name and .version suffix.
- the original file is checked back in and unlocked.
- the new version is uploaded as the parent node of the initial file.
Each time a new version is created it will become the parent node of the previous versions, including the original file which will keep its original name and be the first in the file’s tree. The application has other several functionalities as follows:
- Refresh local file: overwrites the local content of the check-out file with the content from the FTP server. (In the cases that another user modified it’s content and you would like an update)
- History: displays a history of the actions performed over a certain file.
- Undo check-out: unlocks the file without creating a new version.
Following there is a screenshot of the Data-Tracking Client.
![]()
The Data-Tracking Client was develop by Ropardo S.R.L. in the Traser Project. TraSer is an EU FP6 funded project (Information Society Technologies, ICT for Networked Businesses) with a development duration of 3 years (June 2006-May 2009).
Finally, there’s another very important peculiarity of what does Cialis that brings it so high above its alternatives. It is the only med that is available in two versions – one intended for use on as-needed basis and one intended for daily use. As you might know, Viagra and Levitra only come in the latter of these two forms and should be consumed shortly before expected sexual activity to ensure best effect. Daily Cialis, in its turn, contains low doses of Tadalafil, which allows to build its concentration up in your system gradually over time and maintain it on acceptable levels, which, consequently, makes it possible for you to enjoy sex at any moment without having to time it.
