In this post we are going to create RESTfull APIs using PHP framework Symfony 3. This will be exemplified on a “Car” entity.
1. Creating Symfony Application
First make sure you have composer globally installed and then run the next command that will install the latest version of Symfony:
composer create-project symfony/framework-standard-edition my_project
2. Bundles configuration
To implement the web services you will need the following 3 bundles: JMSSerializerBundle, FOSRestBundle, NelmioApiDocBundle. Run the commands from below:
composer require jms/serializer-bundle
composer require friendsofsymfony/rest-bundle
composer require nelmio/api-doc-bundle
After installing them using composer, the 3 bundles must be included in AppKernel.php.
public function registerBundles()
{
$bundles = array(
// ...
new Nelmio\ApiDocBundle\NelmioApiDocBundle(),
new JMS\SerializerBundle\JMSSerializerBundle(),
new FOS\RestBundle\FOSRestBundle(),
);
// ...
}
The next thing to do is register the route for the NelmioBundle in app/config/routing.yml.
NelmioApiDocBundle:
resource: "@NelmioApiDocBundle/Resources/config/routing.yml"
prefix: /api
Now the bundles configurations must be enabled in app/config/config.yml.
nelmio_api_doc:
sandbox:
accept_type: "application/json"
body_format:
default_format: "json"
fos_rest:
param_fetcher_listener: true
body_listener: true
routing_loader:
default_format: json
include_format: false
view:
view_response_listener: true
This configuration is for minimal usage. For more options,please visit the following websites: FOSRestBundle and NelmioApiDocBundle
3. Creating new bundle (CarBundle)
To create a bundle run the next command and follow the installation steps:
php app/console generate:bundle.
As we said this tutorial is based on a “Car” entity. So we need a class “Car” in Entity folder.
namespace CarBundle\Entity;
use Doctrine\ORM\Mapping as ORM;
/**
* @ORM\Table(name="cars")
* @ORM\Entity
*/
class Car
{
/**
* @ORM\Column(type="integer")
* @ORM\Id
* @ORM\GeneratedValue(strategy="AUTO")
*/
private $id;
/**
* @ORM\Column(type="string", length=35)
*/
private $brand;
}
As you can see, Doctrine is used to map the Entitiy to the car table.
The next step is to create a controller (CarController) and register the route in Resources/config/routing.yml.
namespace CarBundle\Controller;
use Sensio\Bundle\FrameworkExtraBundle\Configuration\Route;
use Symfony\Bundle\FrameworkBundle\Controller\Controller;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Request;
use FOS\RestBundle\View\View;
use FOS\RestBundle\Request\ParamFetcher;
use FOS\RestBundle\Controller\Annotations as Rest;
use Nelmio\ApiDocBundle\Annotation\ApiDoc;
class CarController extends Controller
{
/**
* List cars.
*
* @Rest\Get("/cars")
* @Rest\View
*
* @ApiDoc(
* section="cars",
* description="List cars",
* statusCodes={
* 200="Returned when successful",
* 404="Not found"
* }
* )
*
* @return mixed
*/
public function getCarsAction()
{
$cars = $this->getDoctrine()
->getRepository('CarBundle:Car')
->findAll();
return View::create(array("cars" => $cars), 200);
}
}
“getCarsAction()” method returns all records coresponding to Car entity. The web service that callls the method has the route “/cars”.
Resources/config/routing.yml
Cars:
type: rest
prefix: /v1
resource: CarBundle\Controller\CarController
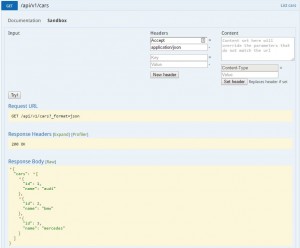
Finally you can see the result in the following image where the webservice is tested and returns a JSON response:
We hope this helps you. Good luck.